Runner Agents
What are runner agents?
Runner agents are responsible for launching Terraform jobs that deploy your infrastructure to the cloud. Tharsis currently offers two different types: Shared runners (which are automatically available to everyone) and group runners (bring your own runner).
Check the FAQ to see if there's already an answer.
Shared runner agents
Shared runner agents are created via the Tharsis API configuration and are available as part of the API's process. By default, if no runner agents are configured at the group level, the shared runner agents will be used instead.
Group runner agents
A runner agent launches Terraform jobs using the configured job executor and authenticates with the Tharsis API using a service account.
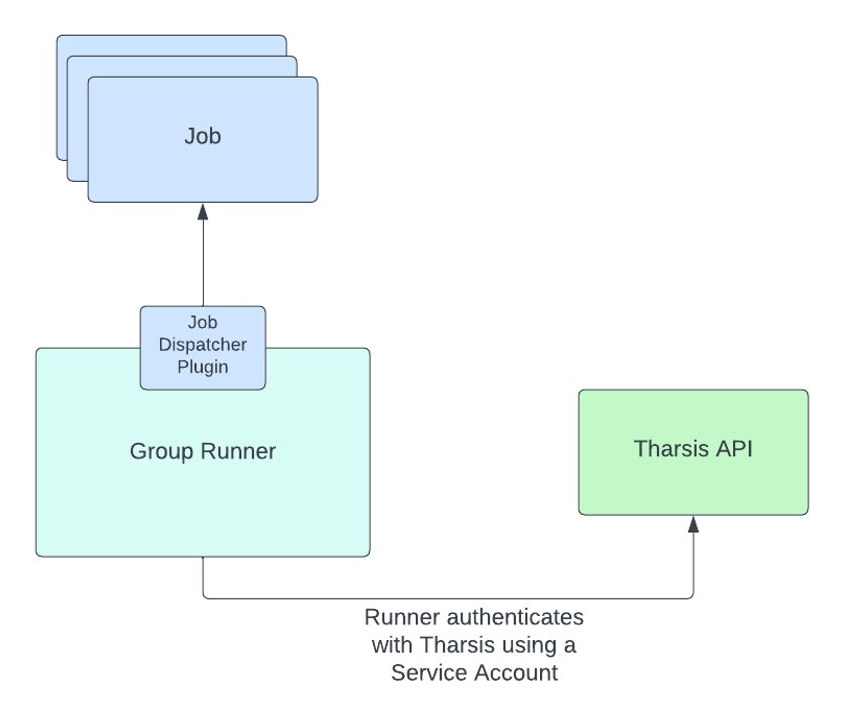
Service accounts are vital for the communication between a runner agent and the Tharsis API. Without them, it wouldn't be possible for a runner agent to claim jobs.
Be sure to assign a service account to your runner agent to ensure proper operation or job(s) may stay queued forever!
How to run a group runner in a container using AWS IAM authentication
In the Tharsis UI, create a service account:
-
Create the service account. The service account must be in a group that is a parent, grandparent, or other direct ancestor of the workspace(s) in which you intend to use the runner. Also, the service account needs to be in the same group or a parent group of the group runner.
-
When creating the trust policy via the "Trusted Identity Providers" box, make a note of the issuer URL. If you are using an IAM role and the iam-oidc-provider for authentication, when you later launch the runner container, in order to facilitate identity-based authentication, the same identity provider/issuer URL will need to be set in the -endpoint option in the THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_ARGS environment variable.
-
Create a bound claim in the trust policy for the service account. For example, if using the "aud" field and the "tharsis" value, assign these values to the fields:
- name: "aud"
- value: "tharsis" When you later launch the runner container, use the -aud option with the same value in the THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_ARGS environment variable.
In the Tharsis UI, create a runner:
-
Create the runner in an ancestor group of the intended workspace.
-
Assign the service account created above to this runner.
Outside Tharsis, launch a runner container:
The runner container runs outside the Tharsis installation.
The recommended container image is named "runner" if building from source. The full registry namespace is "infor-cloud/martian-cloud/tharsis/tharsis-api/runner".
The following environment variable settings are required or recommended:
-
THARSIS_API_URL: This should be the URL to your Tharsis API. -
THARSIS_RUNNER_PATH: This should be the resource path of the runner you created inside Tharsis. -
THARSIS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_PATH: This should be the resource path of the service account you created inside Tharsis. -
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_PATH: If using the iam-oidc-provider, this is the filesystem path to the credential helper binary inside the runner container. If using the recommended "tharsis-api/runner" image, it should be "/opt/credhelpers/iamoidccredhelper" -
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_ARGS: If using the iam-oidc-provider, these are example options if using the iam-oidc-provider and "aud" and "tharsis" in the service account's bound claim's trust policy: -region: the AWS region of your identity provider -endpoint: The URL to your identity provider -aud: This must match the "aud" value in the trust policy in the service account you created inside Tharsis. It can be "tharsis" -
THARSIS_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_HOST: This should be the host name for your service discover host. If using a Tharsis installation accessible via HTTPS, it can be the host name of your Tharsis API. More information about the discover process can be found here: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/internals/remote-service-discovery#discovery-process -
See below for the 'THARSISJOB_DISPATCHER*' variables that will also be needed.
For your runner to access your AWS credentials for authentication with the Tharsis API, you can mount your "~/.aws" directory into the container as a volume.
Example 'docker run' command:
docker run --volume=${HOME}/.aws:/home/nonroot/.aws --env-file=group-runner.env infor-cloud/martian-cloud/tharsis/tharsis-api/runner
Example group runner environment variables file:
THARSIS_API_URL=http://tharsis-api-host:8000
THARSIS_RUNNER_PATH=my-group/my-runner-name
THARSIS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_PATH=my-group/my-service-account-name
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_PATH=/opt/credhelpers/iamoidccredhelper
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_ARGS=-region=us-east-2 -endpoint=https://my-oidc-provider-host -aud=tharsis
THARSIS_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_HOST=my-service-discovery-host
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_TYPE=local
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_API_URL=http://tharsis-api-host:8000
Environment variables to configure a runner agent
The following environment variables are required for configuring a runner agent:
| Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
THARSIS_RUNNER_PATH | Full path to the runner agent. For example, spectre/spaceship/impatient. |
THARSIS_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_PATH | Full path to the service account the runner will use to interact with the API. |
THARSIS_API_URL | URL to the Tharsis API instance. |
THARSIS_SERVICE_DISCOVERY_HOST | Host for service discovery. Generally, the same host as the Tharsis UI. |
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_PATH | Path to the IAM OAuth credential helper. Runner agent will invoke this binary to retrieve an initial token from an OAuth provider to create a service account token. |
THARSIS_CREDENTIAL_HELPER_CMD_ARGS | Arguments for the IAM credential helper binary. Currently, it requires: --region (default: us-east-1), --endpoint (service endpoint), and --aud (audience). |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_TYPE | Job dispatcher type. Choose from ecs, kubernetes, docker or local (for local instances). |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_API_URL | Tharsis API URL. |
Elastic Container Service (ECS)-specific environment variables
| Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_TASK_DEFINITION | Amazon Resource Name (ARN) for the job executor. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_REGION | AWS Region where job executor is located. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_CLUSTER | AWS ID of the Elastic Container Service (ECS) cluster. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_SUBNETS | Job dispatcher subnets passed in as comma separated values. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_LAUNCH_TYPE | For ecs job dispatcher type, choose from ec2 or fargate. |
Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)-specific environment variables
| Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_AUTH_TYPE | Auth type. Choose from eks_iam. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_IMAGE | Docker image for the job executor. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_MEMORY_REQUEST | Amount of memory to request for runner agent jobs. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_MEMORY_LIMIT | Memory limit for runner agent jobs. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_NAMESPACE | Optional Kubernetes namespace. default otherwise. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_REGION | EKS region to use for IAM Auth. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_EKS_CLUSTER | Name of the EKS cluster. |
Docker-specific environment variables
| Name | Meaning |
|---|---|
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_HOST | Docker client host. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_IMAGE | Docker image for the job executor. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_LOCAL_IMAGE | Boolean value indicating if job executor's Docker image is local. Choose from true, false or alike. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_EXTRA_HOSTS | Extra hosts passed in as a comma-separated list. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_MEMORY_LIMIT | Memory limit for the job dispatcher. Example: 42 MB. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_BIND_PATH | Volume binding for the Docker container. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_REGISTRY_USERNAME | Username for the Docker registry. |
THARSIS_JOB_DISPATCHER_DATA_REGISTRY_PASSWORD | Password for the Docker registry. |
Not all of these environment variables are always required. Depending upon the configuration and dispatcher type, only a few values may be needed.
Runner agent precedence
Tharsis defines a precedence for the way runner agents may claim jobs. In particular, runner agents are given priority in the following order:
- Group runner agent is available in the same group as the job's workspace. For example, a runner agent
spectre/spaceship/impatientwill be given priority for a job in workspacespectre/spaceship/phantomas they both have the same parent groupspectre/spaceship. - Group runner agent is an ancestor (in a parent group) of the job's workspace. Tharsis API will use the nearest available runner agent.
- No runner agents are available in an immediate or parent group; A shared runner agent will be used instead (default).
Group runner agents within the job's workspace hierarchy are given precedence; otherwise, a shared runner is used.
Built-in environment variables
The following environment variables are made available via Tharsis' job executor:
THARSIS_GROUP_PATH: full resource path of the group the job is executing inside.THARSIS_ENDPOINT: URL to the Tharsis API instance.TF_TOKEN_<api_host>: used by Tharsis Terraform Provider.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
How can I create or modify a group runner agent?
Currently, there are two ways: The Tharsis CLI's runner-agent command or the Tharsis UI's runner agents page at the group level.
Why can't I assign a service account to a shared runner agent?
Shared runner agents are available on an as-is basis and cannot be modified by anyone except a system administrator. This includes not being able to assign/unassign service accounts to/from the shared runner agent respectively.
Can I create or modify a shared runner agent?
No. Shared runner agents can only be created via the API's configuration file and cannot be altered except by a system administrator.
What does a service account help a runner agent do? Do I have to assign a service account?
Service accounts are essential for a runner agent to authenticate with the Tharsis API for claiming jobs, among other things. The need for managing static secrets, such as tokens or registration keys, is eliminated as service accounts replace it with OIDC federation.
What is a service account and how do I create one?
We're glad you asked! See here.
What job dispatcher types does the jobs executor plugin support?
As of yet, AWS ECS, Kubernetes, and Docker are supported.