Managed Identities
What are managed identities?
Managed identities are used to assume cloud provider credentials using OIDC federation. They provide credentials to the Terraform providers without having to store credentials.
Tharsis supports Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Kubernetes managed identities for assuming IAM roles, Azure Service Principals, and Kubernetes roles respectively. These managed identities can be created in a group via the UI and assigned to a workspace for deploying resources.
The Tharsis CLI includes a --managed-identity flag to automatically assign the given managed identity to a workspace when it's created, meaning a workspace is ready to go with just one command!
Once a managed identity is created in a Tharsis group, it is inherited by all its child groups. Just be sure to assign it to the workspace!
Check the FAQ to see if there's already an answer.
Create a managed identity
AWS Managed Identity
-
Create an OpenID Connect identity provider in the AWS account where the IAM role will be linked to the managed identity.
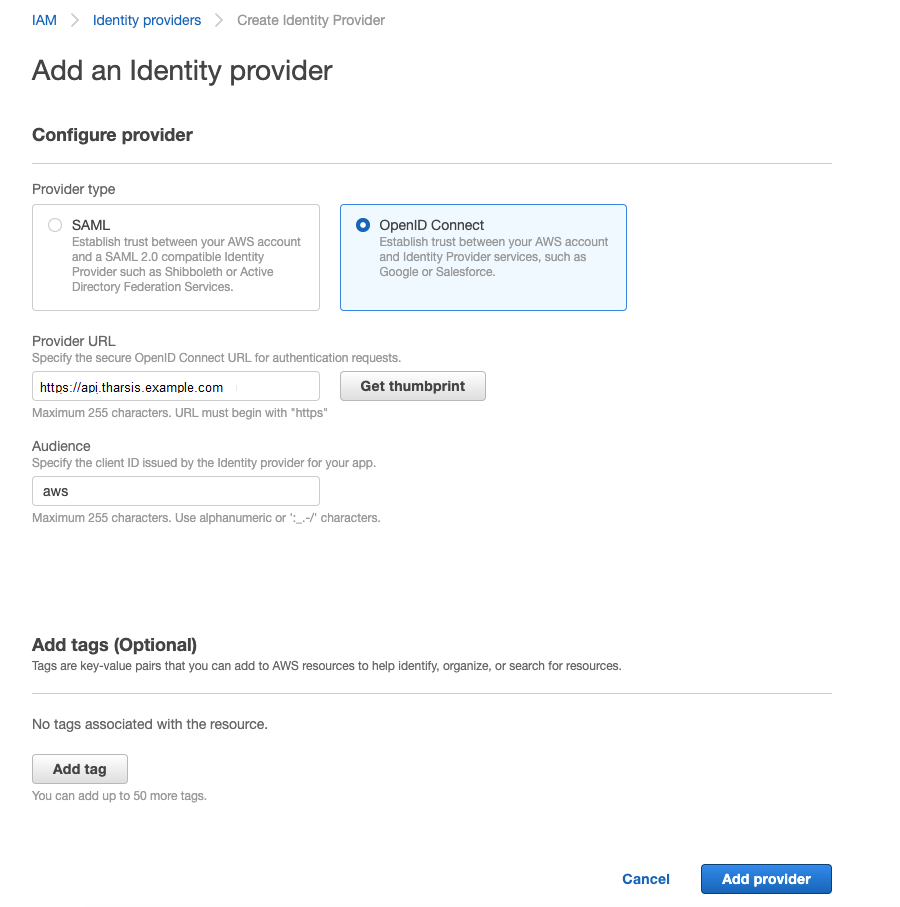
Enter Provider URL:
https://api.tharsis.example.com, and Audience:aws. ClickAdd provider. -
Create the managed identity in the appropriate Tharsis group:
Extra step for a group's first managed identity
From the group details page, click
Managed Identitieson the left sidebar and thenNEW MANAGED IDENTITY: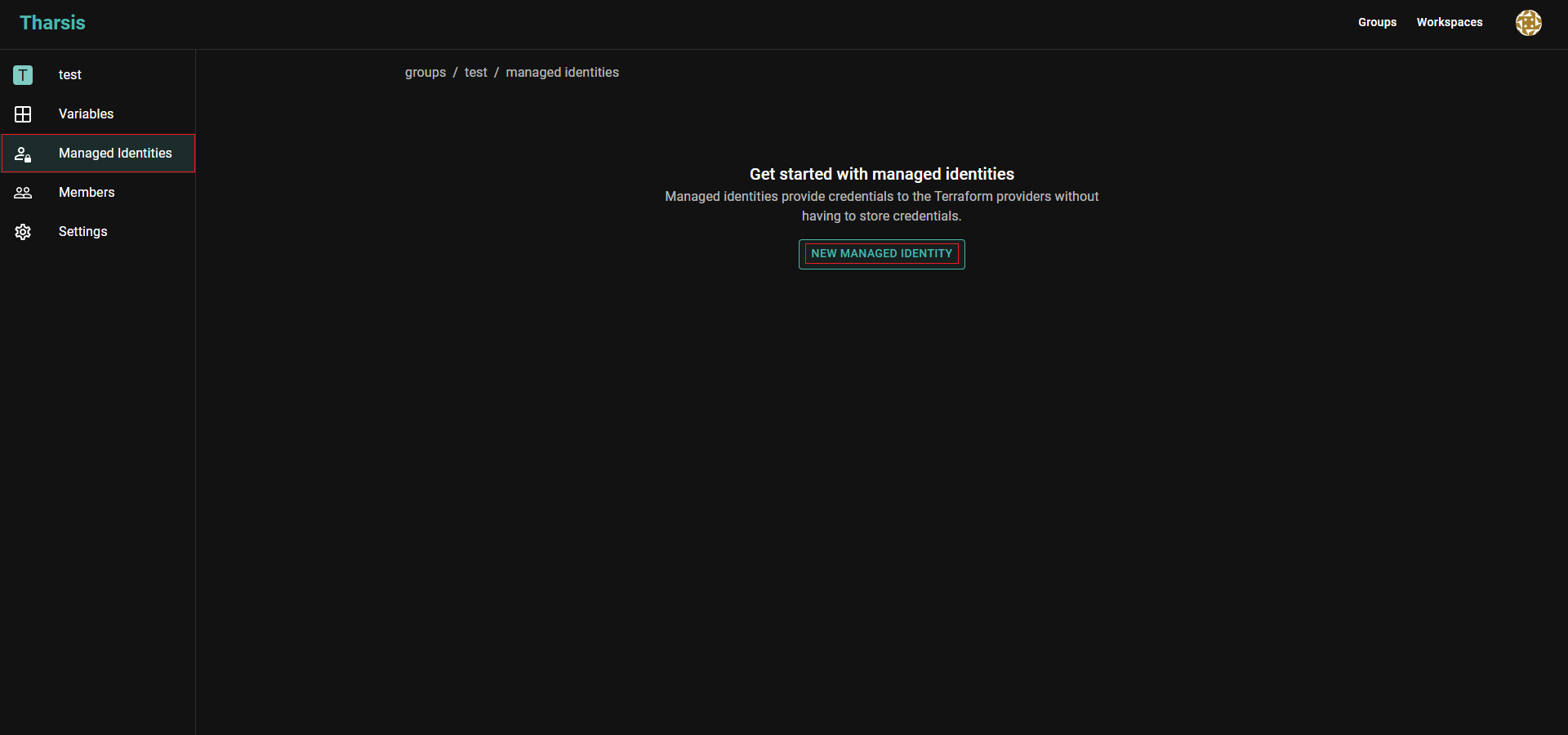
-
Select
AWSas type, provide a name, optionally a short memorable description, the IAM role for provider configuration, and click onCREATE MANAGED IDENTITY: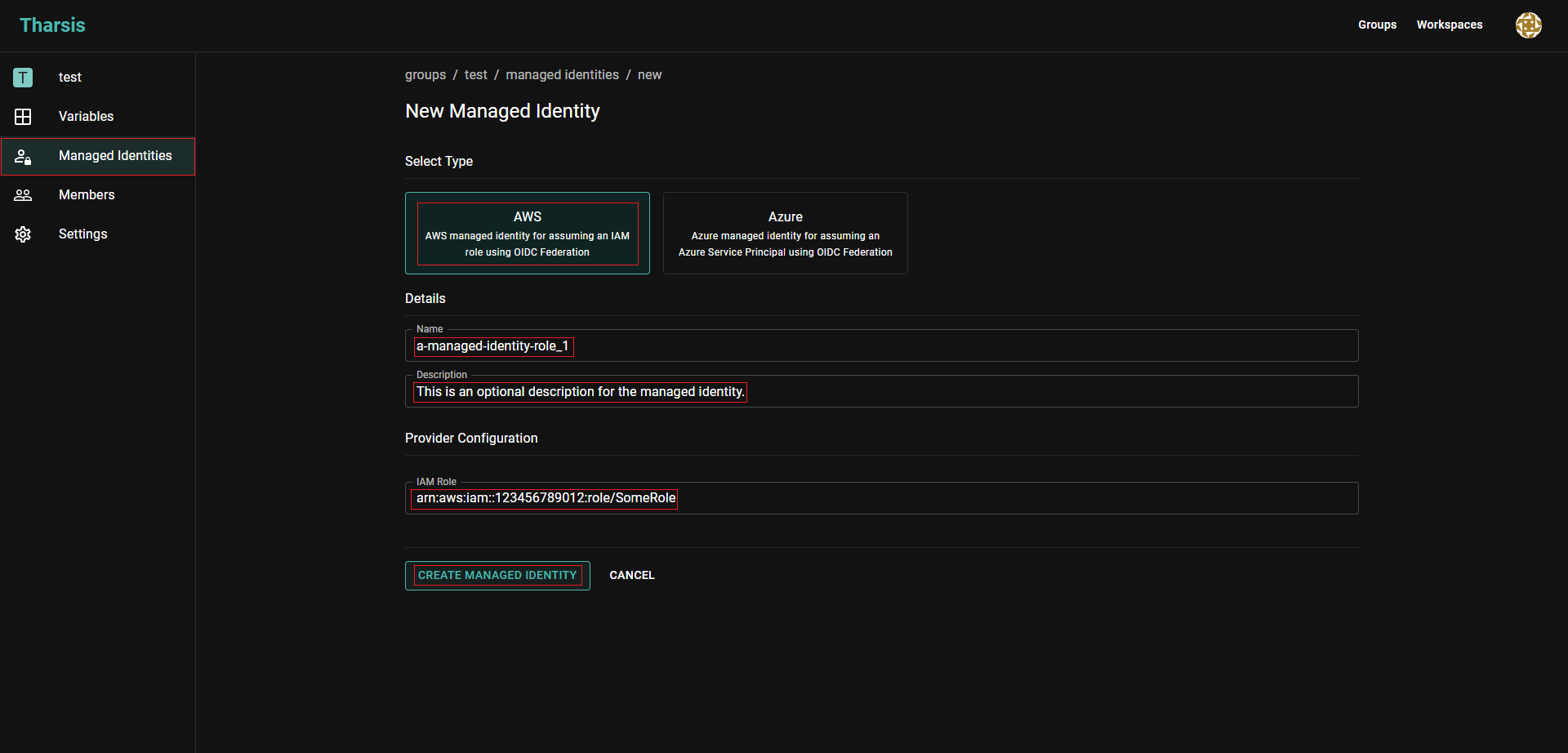 caution
cautionManaged identity names may only contain digits, lowercase letters with a hyphen or an underscore in non-leading or trailing positions.
A managed identity's name cannot be changed once created. It will have to be deleted and recreated, which is dangerous.
-
Once an identity is created, copy the
IAM Trust PolicyTharsis provides and add it to the IAM role in AWS. -
The managed identity can now be assigned to any workspace within the group.
-
-
Azure Managed Identity
-
Create an app registration in Azure.
-
Create the managed identity in the appropriate Tharsis group:
Extra step for a group's first managed identity
From the group details page, click
Managed Identitieson the left sidebar and thenNEW MANAGED IDENTITY:
-
Select
Azureas type, provide a name, optionally a short memorable description, the Client ID, Tenant ID, and click onCREATE MANAGED IDENTITY: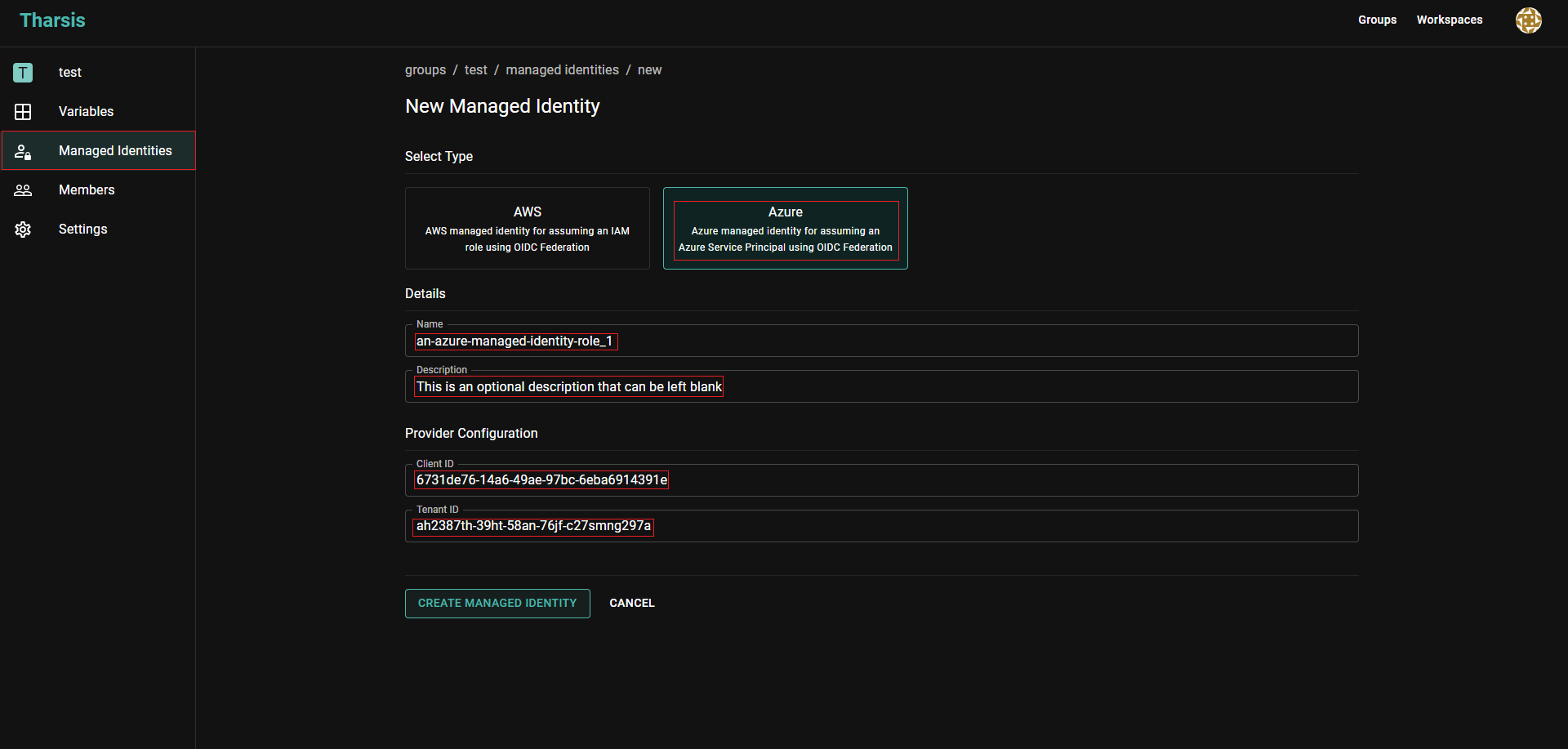 caution
cautionManaged identity names may only contain digits, lowercase letters with a hyphen or an underscore in non-leading or trailing positions.
A managed identity's name cannot be changed once created. It will have to be deleted and recreated, which is dangerous.
-
Once created, the
Issuer,Audience, andSubjectwill be displayed in Tharsis. In the Azure portal, select your app registration. UnderCertificates & Secrets->Federated Credentialsselect theAdd Credentialsbutton and provide theIssuer,Audience, andSubjectfields. -
The managed identity can now be assigned to any workspace within the group.
-
Kubernetes Managed Identity
Step 1: Create the managed identity in Tharsis
-
Select
Kubernetesas type, provide a name, optionally a short memorable description, the audience (or go for default "kubernetes"), and click onCREATE MANAGED IDENTITY: caution
cautionManaged identity names may only contain digits, lowercase letters with a hyphen or an underscore in non-leading or trailing positions.
The Audience field has specific validation rules:
-
Maximum 100 characters
-
No spaces allowed
-
Only alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), and dots (.) allowed
-
Examples:
kubernetes,prod-cluster,cluster.example.com
A managed identity's name cannot be changed once created. It will have to be deleted and recreated, which is dangerous.
-
-
Once created, copy the
Subject(managed identity ID) from the Tharsis UI - you'll need this for the next step. -
The managed identity can now be assigned to any workspace within the group.
Step 2: Configure your Kubernetes cluster with Terraform
Set up both the OIDC identity provider and ClusterRoleBinding in your Terraform configuration:
provider "aws" {
region = var.cluster_region
}
data "aws_eks_cluster" "this" {
name = var.cluster_name
}
data "aws_eks_cluster_auth" "this" {
name = var.cluster_name
}
provider "kubernetes" {
host = data.aws_eks_cluster.this.endpoint
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(data.aws_eks_cluster.this.certificate_authority[0].data)
token = data.aws_eks_cluster_auth.this.token
}
resource "aws_eks_identity_provider_config" "tharsis_oidc" {
cluster_name = var.cluster_name
oidc {
identity_provider_config_name = "${var.cluster_name}-tharsis-oidc"
issuer_url = "https://example.tharsis.com"
client_id = var.audience # Use audience as client_id
username_claim = "sub"
}
}
# Create ClusterRoleBinding for the managed identity
resource "kubernetes_cluster_role_binding_v1" "tharsis_managed_identity" {
metadata {
name = "tharsis-cluster-access-role-binding"
}
role_ref {
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
kind = "ClusterRole"
name = "cluster-admin" # Adjust permissions as needed
}
subject {
kind = "User"
name = "${var.tharsis_oidc_issuer_url}#${var.managed_identity_id}"
api_group = "rbac.authorization.k8s.io"
}
}
Variables to configure:
audience: Your desired value (e.g.,kubernetes)managed_identity_id: The Subject copied from Tharsis in Step 1tharsis_oidc_issuer_url: Your Tharsis instance URL
Update a managed identity
-
From the group details page, click
Managed Identitieson the sidebar and select the appropriate managed identity:
-
Click on
EDIT: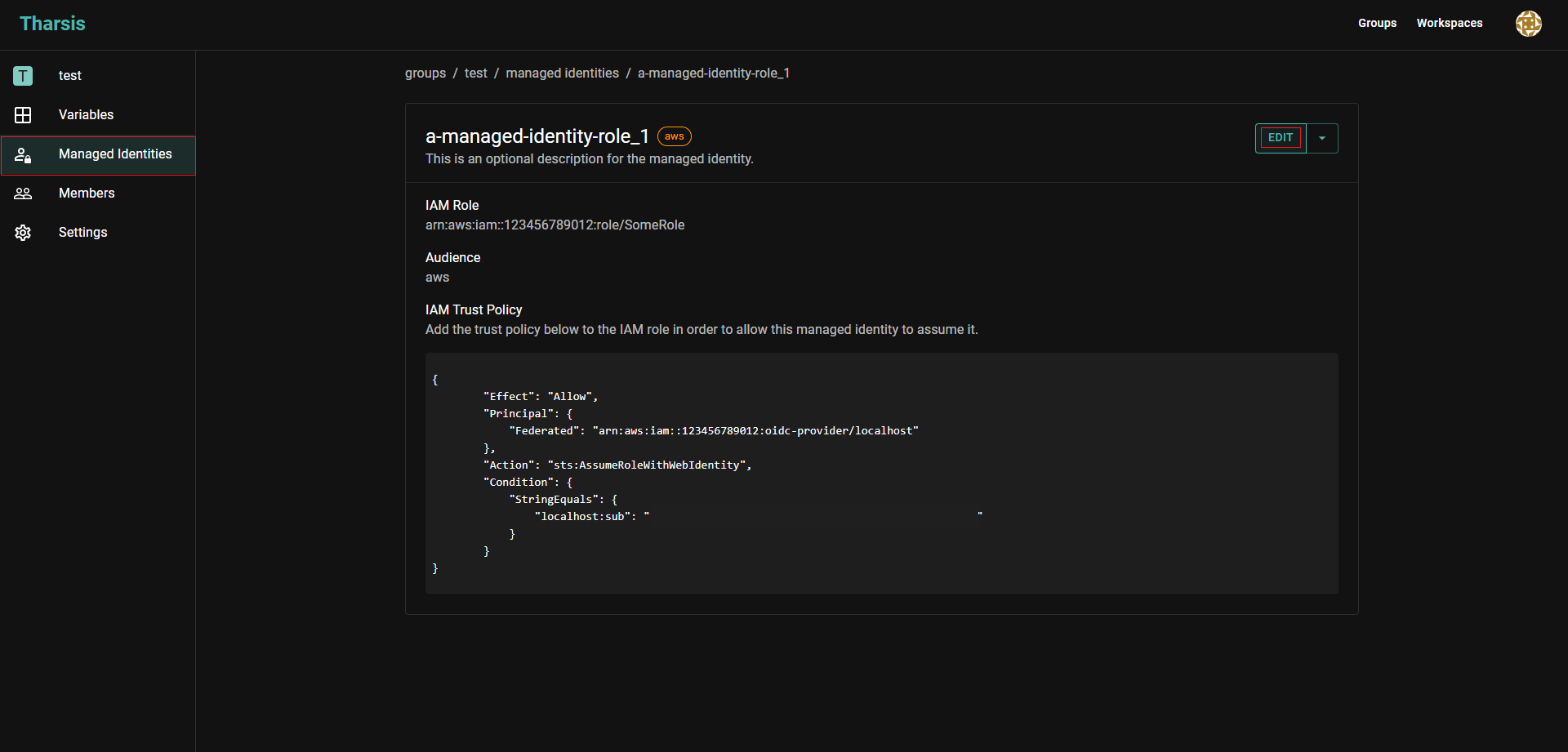
-
Now the description and provider configuration can be updated.
Delete a managed identity
-
From the group details page, click
Managed Identitieson the sidebar and select the appropriate managed identity:
-
Click on ▼ next to
EDIT, thenDelete Managed Identity: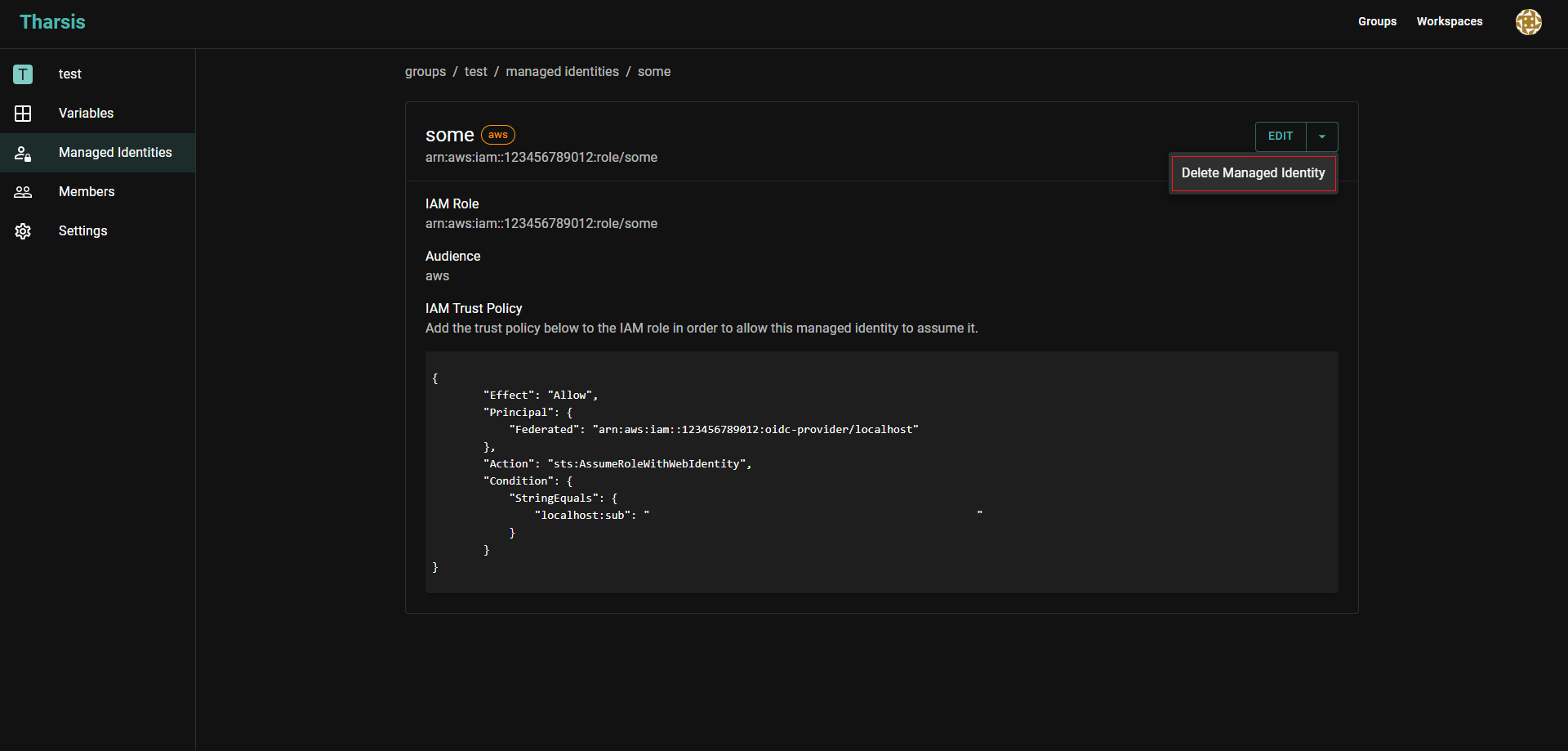 Deletion is dangerous
Deletion is dangerousDeleting a managed identity is an irreversible operation. Proceed with extreme caution.
Assign a managed identity
-
Navigate to the workspace where this managed identity will be used, and click on
Managed Identitieson the left sidebar and search for a managed identity in the search box.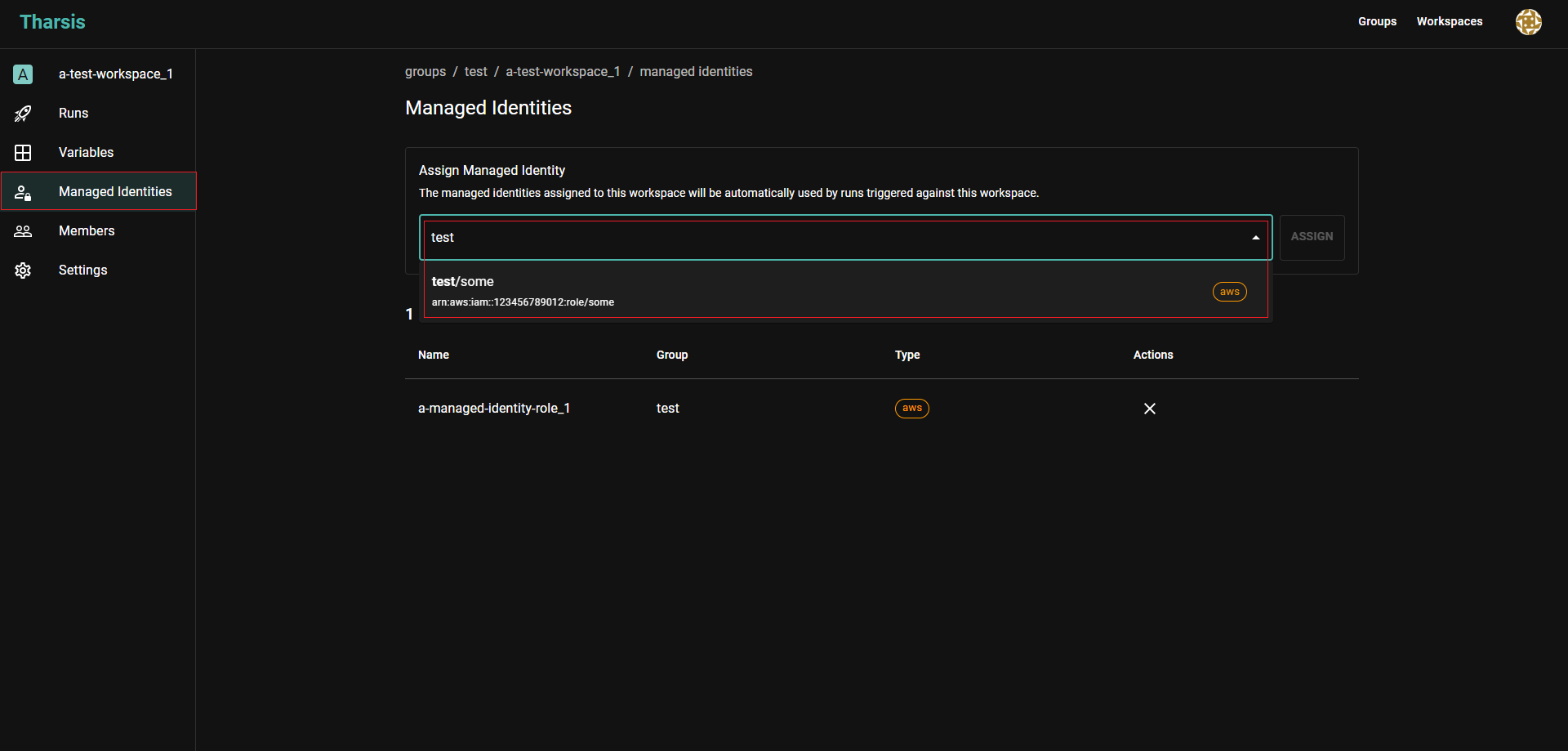
-
Select the appropriate managed identity and it is now assigned to the workspace.
Assign multiple managed identities
Tharsis supports the ability to assign multiple AWS managed identities to a workspace. However, to make use of them, the provider configuration must be updated to use the correct identity.
Expand for a sample Terraform configuration
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.70.0"
}
null = {
source = "hashicorp/null"
version = "~> 3.2.3"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
alias = "data-provider"
region = "us-east-2"
profile = "my-group/identity-two"
}
provider "null" {}
resource "null_resource" "download_s3_file" {
triggers = {
always_run = "${timestamp()}"
}
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = <<EOF
set -e
# Where the AWS CLI is installed to. Must use full path or won't resolve.
CLI_BINARY="/home/tharsis/.local/bin/aws"
echo "Installing AWS CLI"
pip3 install --user --no-cache-dir awscli
"$CLI_BINARY" --version
# Download the file from S3
"$CLI_BINARY" --profile my-group/identity-one s3 cp s3://data/large_file.zip ${path.module}/large_file.zip
EOF
interpreter = ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
}
}
resource "aws_s3_object" "object" {
bucket = "consolidated-bucket"
key = "large_file_copy.zip"
source = "${path.module}/large_file.zip"
depends_on = [null_resource.download_s3_file]
provider = aws.data-provider
}
Let's break down the configuration:
- The
awsprovider is aliased todata-providerand theprofileis set tomy-group/identity-two. This is the resource path of the managed identity in Tharsis. - The
nullprovider is used to download the file from S3 using themy-group/identity-oneprofile. - The
aws_s3_objectresource uses thedata-providerprovider to upload the file toconsolidated-bucket.
The profile attribute in the aws provider configuration is set to the managed identity's resource path. This is how Terraform knows which credentials to use. The alias attribute can be used to differentiate between different AWS provider instances. The provider attribute in the aws_s3_object resource is set to the alias of the provider.
Failure to set the profile attribute when multiple AWS managed identities are assigned to a workspace will result in an error during the Terraform plan/apply phase.
Access rules
While managed identities are really powerful on their own, the addition of access rules takes things a step further and allows fine-grained control on who or what can assume the credentials of the identity. In order for someone/something to use a managed identity, the access rules (if specified) must be satisfied.
Access rules can be created when a managed identity is created or edited in the UI.
Tharsis, by default, allows anyone with deployer access to a managed identity to assume it. So, if you wish to limit access to an identity, formulate the access rules accordingly.
Rule evaluation
Access rules of the same type (either eligible principals or module attestation) use an OR condition, meaning, the first one that matches, passes. However, if rules of multiple types are specified (eligible principals and module attestation) then they use an AND condition, meaning, at least one rule from each access rule type must match successfully.
As of now, there are currently two different types:
- Eligible principals
- Module attestations
Eligible principal rules
Eligible principal rules are meant to limit the usage of a managed identity to a certain set of principals or users/service accounts. There might be use-cases where particular individuals or service accounts should assume a managed identity for creating speculative plans, but not applying them. To address this, Tharsis allows assigning a set of principals to plan and apply stages separately.
Tharsis, by default, will allow any principal to assume a managed identity if an access rule is not defined for that run stage.
Module attestation rules
Module attestation rules prohibit a module from assuming a managed identity unless it has an attestation signed with a public key defined on the access rule. Like eligible principal rules, these rules can also be defined separately for plan and apply run stages and only root modules that satisfy the attestation policy will be allowed.
We're glad you asked! See here for more information.
Managed identity module attestation rules only support modules in the Tharsis registry!
Aliases
Perhaps you've run into a situation where your workflow requires the same managed identity under a different namespace or a parent group and creating a duplicate is not practical—that's where aliases come in. Aliases are resources that allow using a managed identity's data and access rules without the need to duplicate the data and still permit inheritance. They can be used just like a regular managed identity.
Aliases can be...
- Resources with their own unique name.
- Inherited like any managed identity.
- Shared with a parent or sibling group.
- Deleted if the principal is an owner in either the source identity's or alias' group.
Aliases cannot be...
- Created for namespaces the source managed identity* is already available under through inheritance.
- Updated and must use the same data from the source managed identity.
- Created unless the principal is an owner of both the source identity's and alias' groups.
*Source managed identity refers to the identity being aliased.
Creating an alias
To create an alias, navigate to the target group's details page and click on Managed Identities on the left sidebar. Then click on the Aliases tab and select CREATE ALIAS. Give it a name and search for the group where the alias should be available and hit CREATE ALIAS. The alias is now available in the target group and can be assigned to a workspace.
An alias' data is inherited from the source managed identity and cannot be updated. Any changes to the source managed identity will be reflected in the alias.
Deleting an alias
To delete an alias, navigate to the target group's details page and click on Managed Identities on the left sidebar. Then click on the Aliases tab and select the alias to be deleted. Select the alias and once on the alias details page, click on the DELETE ALIAS button. The alias is now deleted.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Who can create/update/delete managed identities?
- Owner role can modify managed identities.
- Deployer or lower cannot modify managed identities.
Can multiple managed identities of the same type be created in a group?
Yes, you can create multiple AWS managed identities within a group and assign them to a workspace. However, non-AWS managed identity types are restricted to one per workspace. For more details, refer to Assign multiple managed identities.
Is there a way to "mask" managed identities to prevent inheritance?
Managed identity access rules can be used to limit who may assume the identity, which achieves a similar effect.
When do I need to use AWS profiles in the Terraform provider configuration?
When multiple AWS managed identities are assigned to a workspace, the profile attribute in the provider configuration must be set to the managed identity's resource path. For more information, see Assign multiple managed identities.
Can I still assign other managed identities types if multiple AWS managed identities are assigned to a workspace?
Yes, other managed identity types like Azure, Tharsis, etc., can still be assigned to a workspace but they're limited to one per workspace.