Tharsis - The Open-Source Terraform Platform
We are excited to announce a new open-source Terraform platform called Tharsis! Tharsis is a free open-source project that offers an alternative to using the HashiCorp Terraform Cloud Platform (HCP). It's an enterprise-scale Terraform platform that offers a complete solution for managing your Terraform deployments, state, and workspaces. Tharsis is licensed under the MPL license and can be used for free on your machine or can be deployed to your own cloud infrastructure so that your entire team can benefit from using it.
The demo video below shows how Tharsis can be used to quickly deploy a module, view the Terraform plan, and apply the infrastructure change all from the Tharsis UI. For those who prefer using the CLI to trigger deployments, Tharsis is compatible with the Terraform CLI, and we provide a Tharsis CLI as well, which has some extra Tharsis-specific features.
If you'd like to jump right in and start using Tharsis, check out our quickstart guide
Features
Tharsis includes everything you need to manage and deploy IaC using Terraform at scale. Some of the key features include:
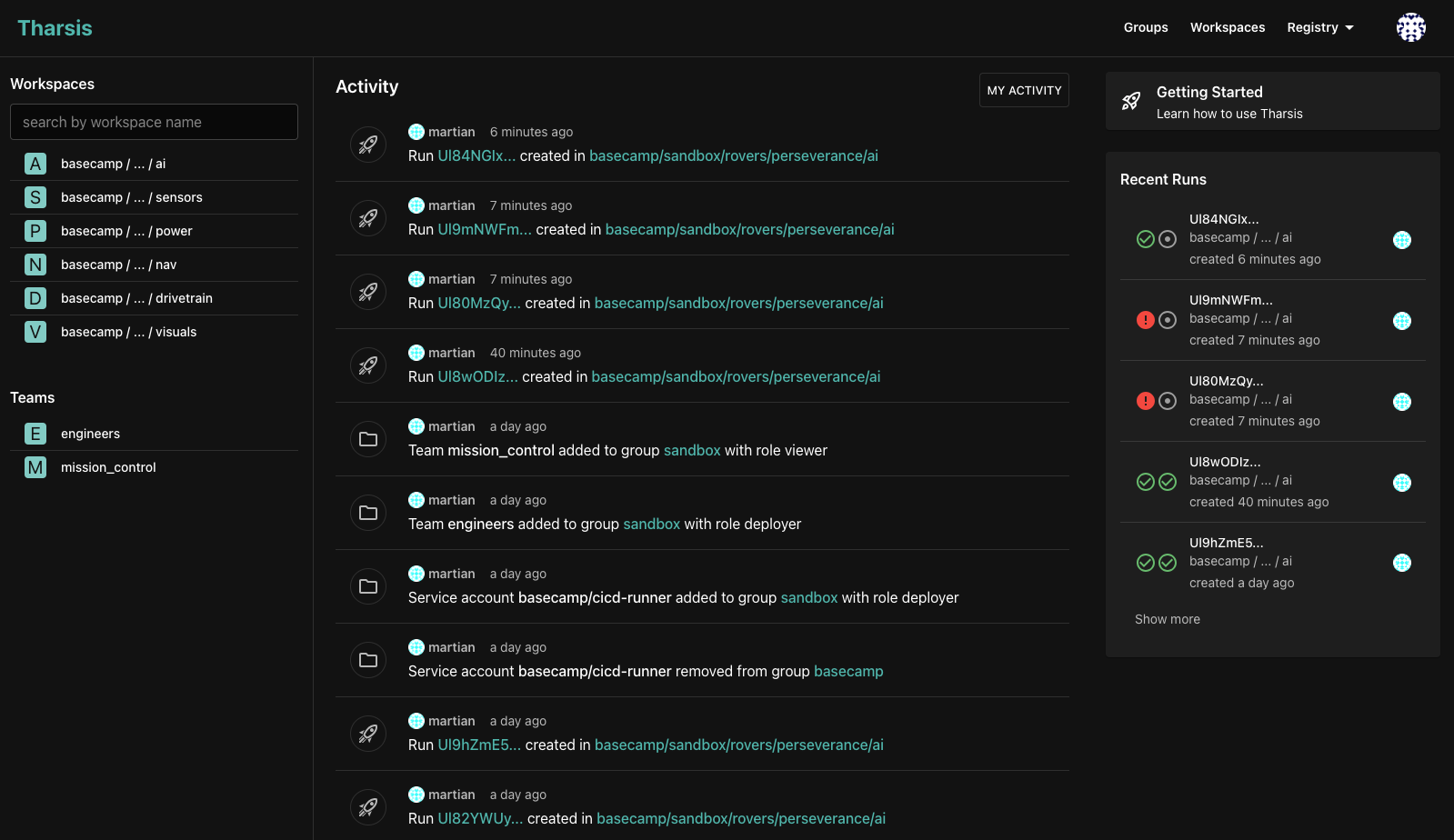
Home Dashboard
As infrastructure and deployments increase in complexity, it's important to have a single dashboard that provides all the information you need to manage your deployments. The Tharsis home dashboard provides this information by displaying the status of your latest runs, the workspaces that you have access to, recent activity events, and the teams that you're a member of.
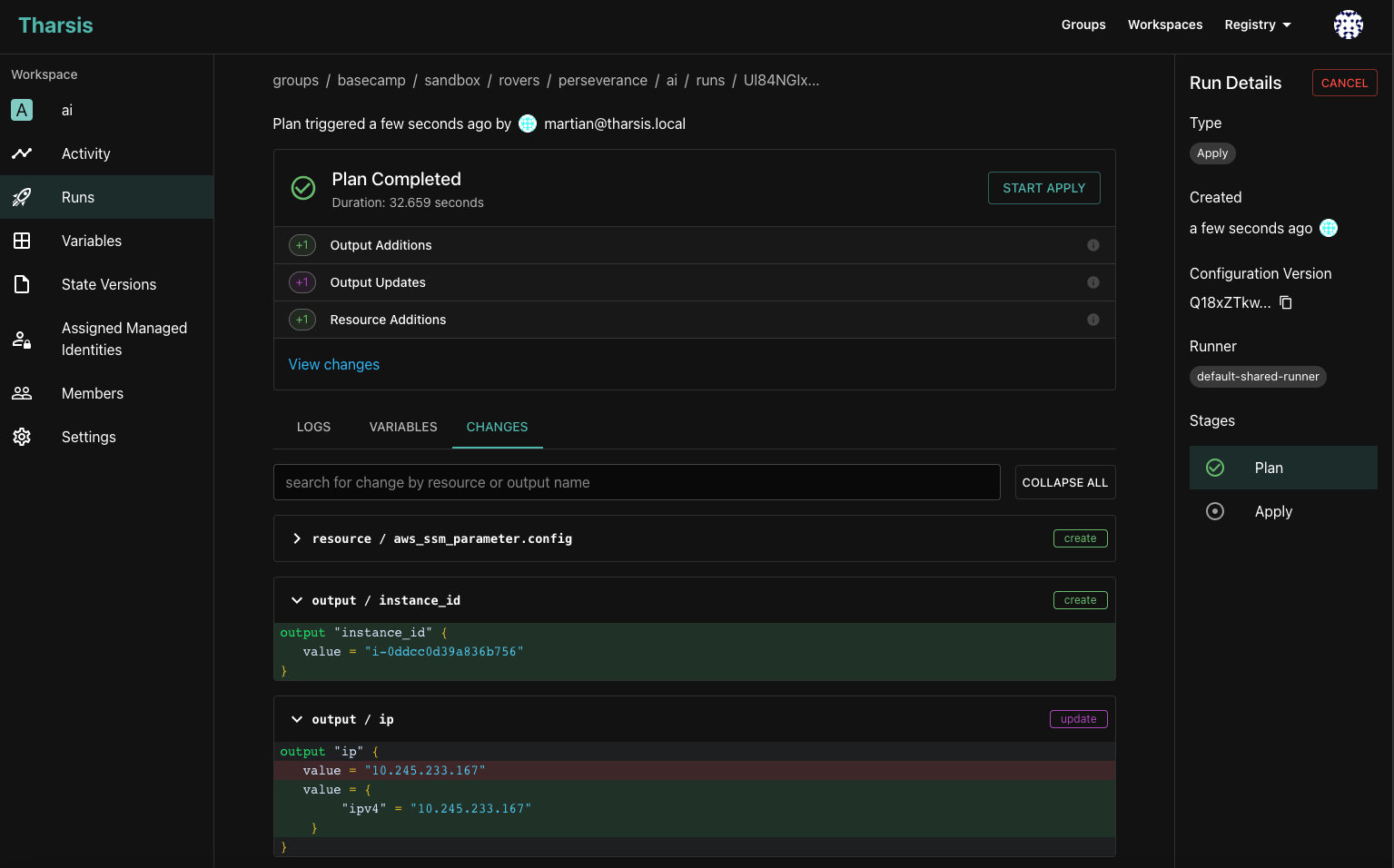
Terraform Runs With Plan Visualization
When creating a Terraform run, it's important to understand what changes will be made to your infrastructure. In addition to showing the streaming logs as a run is in progress, Tharsis also provides a visual diff of the changes that will be applied to your infrastructure. This makes it easy to understand what changes will be made before applying them without having to dig through the logs.
A plan summary is also displayed, which shows the number of resources and outputs that will be created, updated, destroyed, and imported. Any resources that have drifted will also be labeled as such so that you can easily see what resources are out of sync with your Terraform state.
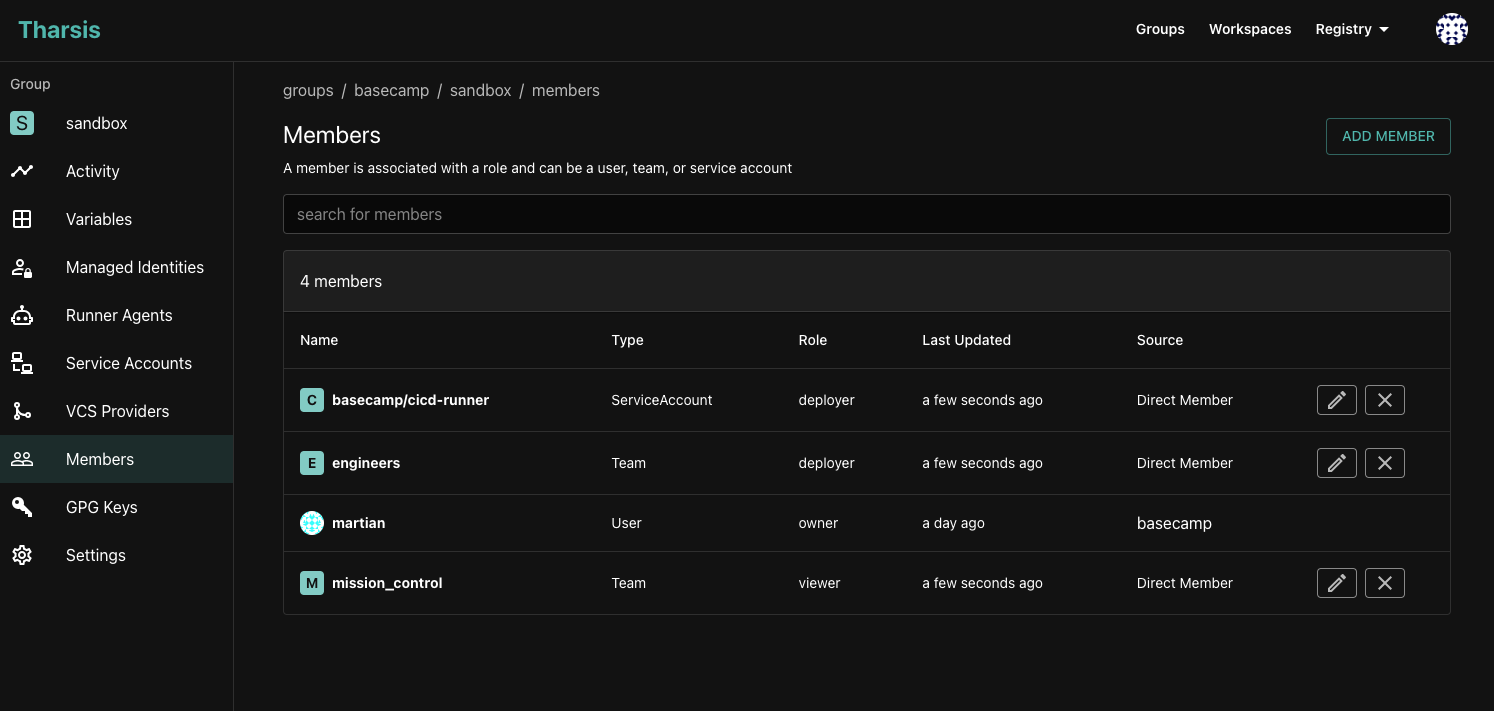
Role-Based Access Control
RBAC is a key feature of Tharsis that allows you to control who can view, deploy, and manage your infrastructure. Out of the box, Tharsis provides three roles: viewer, deployer, and owner. Roles can be assigned at the group or workspace level, and they determine what actions a user or service account can perform within the group or workspace.
The screenshot below shows an example of the members assigned to the sandbox group. Three of the members are assigned directly to the group, while the martian member is inherited
from the basecamp group. In this example, the martian user has owner permissions within any workspace under the basecamp group, while the other members only have the assigned permissions
within the sandbox group. This shows how the group hierarchy and inheritance can be used to simplify permission management by allowing permissions to be set at the group level and inherited
by subgroups.
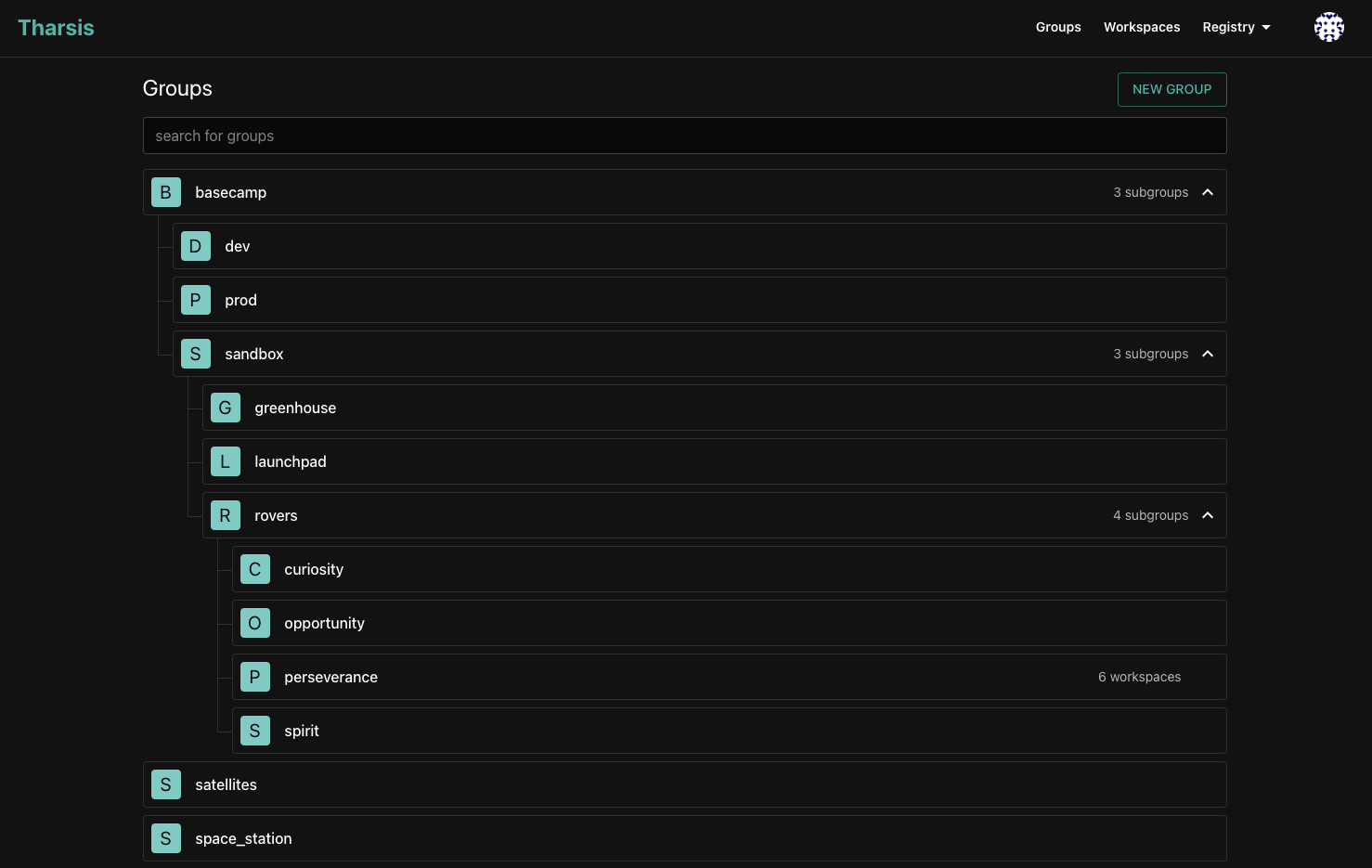
Group Hierarchy
Use a group hierarchy to organize your workspaces in a way that makes sense for your organization. You can create groups and subgroups to model your product and environment structure. Terraform variables set at the group level will be inherited by all workspaces in that group.
In the screenshot below, you can see an example of a group hierarchy with multiple subgroups. The basecamp group contains three subgroups: sandbox, dev, and prod.
The various components that are deployed to each environment are then contained within subgroups under the environment group. This allows workspaces to be organized in a
way that makes sense for your organization and product.
Permissions can also be set at the group level, allowing you to control who can view, deploy, and manage the infrastructure within the group or its subgroups. A user, service account, or team can be assigned a role at the group level, and that role will determine what permissions the subject has within the group and its subgroups.
Terraform Provider and Module Registry
Tharsis provides a built-in Terraform registry that allows you to easily manage your private Terraform providers and modules. The registry is a central location where you can store, discover, and share your Terraform providers and modules with your team. You can publish to the registry using the Tharsis CLI, and then deploy modules to your workspaces without having to worry about managing the module source code during deployments. The registry also allows you to version your modules, making it easy to track changes and roll back to a previous version if needed. When publishing, you can set the visibility to public or private, allowing you to control who can access and use the provider or module.
No Code Deployments
Tharsis provides the ability to deploy your Terraform modules to a workspace via the Tharsis CLI or UI without writing any code. For example, you can create a module in the Tharsis registry with a specific version, and then deploy that module to a workspace without having to write any Terraform code. This is useful for deploying common infrastructure and configurations without having to create a root Terraform config to wrap the module.
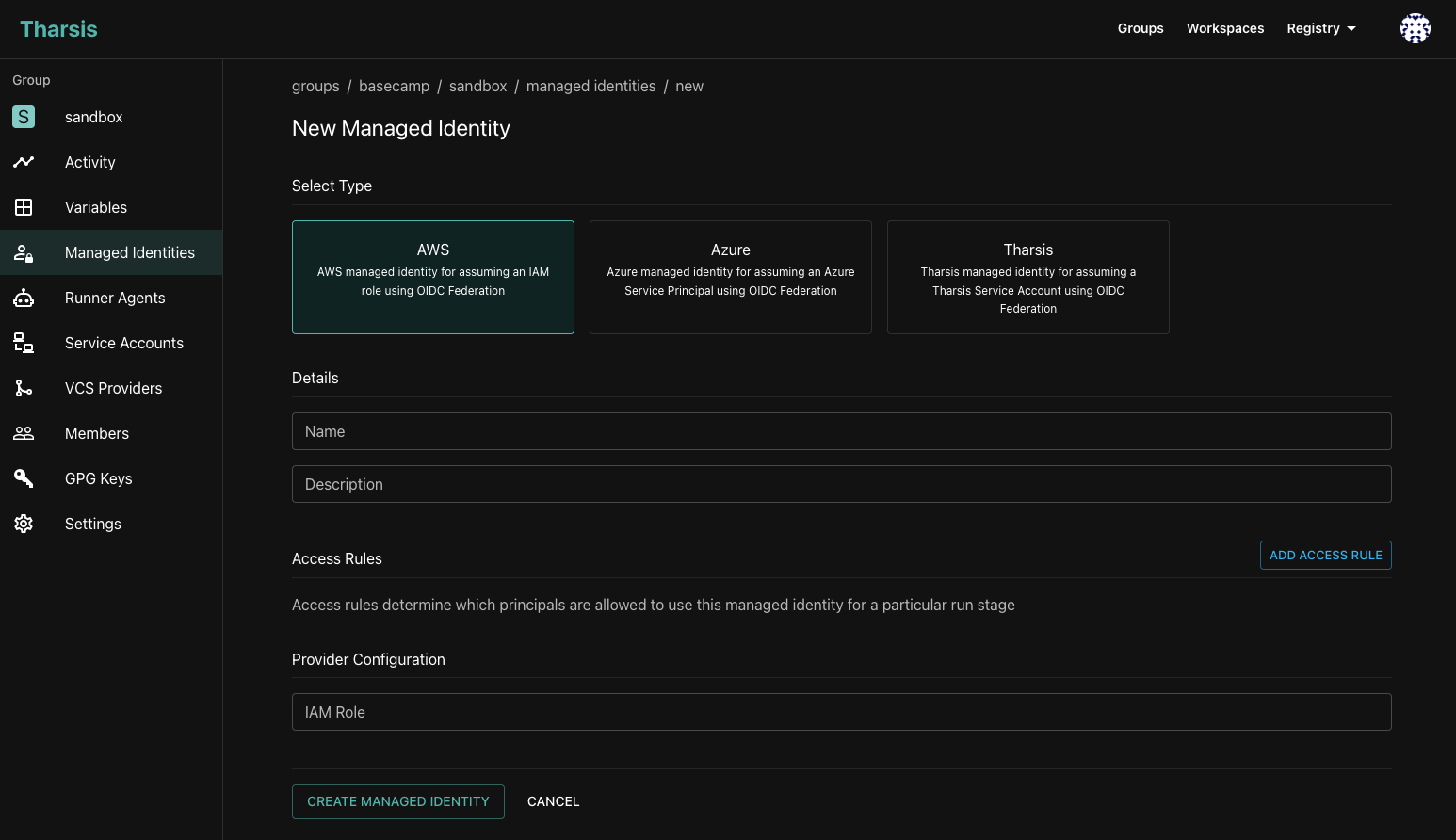
Managed Identities
Managed identities allow you to securely authenticate with your cloud provider without exposing your credentials. Managed identities are currently supported for AWS and Azure. OpenID Connect (OIDC) is used to authenticate with the target cloud providers, eliminating the need to store static credentials. Managed identities also allow you to set an access control policy to restrict how the managed identity can be used. Currently, there are two types of access control policies: eligible principals and module attestation. The eligible principals policy allows you to restrict which users, teams, or service accounts can use the managed identity. The module attestation policy allows you to restrict which modules can be deployed using the managed identity by requiring that the Terraform module be attested using the In-toto Attestation Framework.
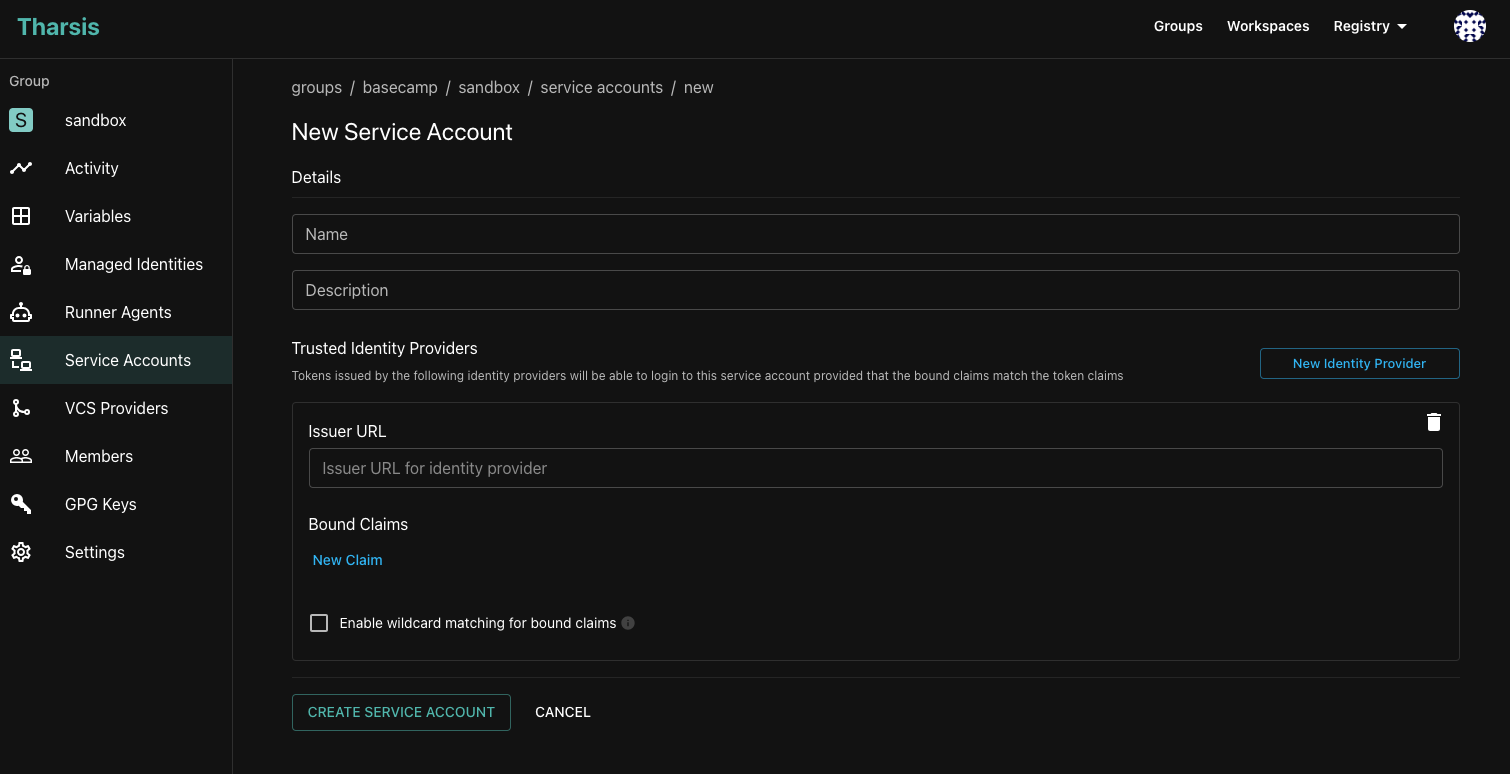
Service Accounts
Service accounts are useful for triggering Terraform deployments from CI/CD pipelines or other automated workflows where machine-to-machine authentication is required. Service accounts can be created in Tharsis and assigned a role within a group or workspace similar to a user. To avoid having to store static secrets such as API keys, service accounts use OIDC as the authentication mechanism. This allows CI/CD runners such as GitHub Actions or GitLab Jobs to assume a service account using a JWT token that is compatible with the OIDC protocol.
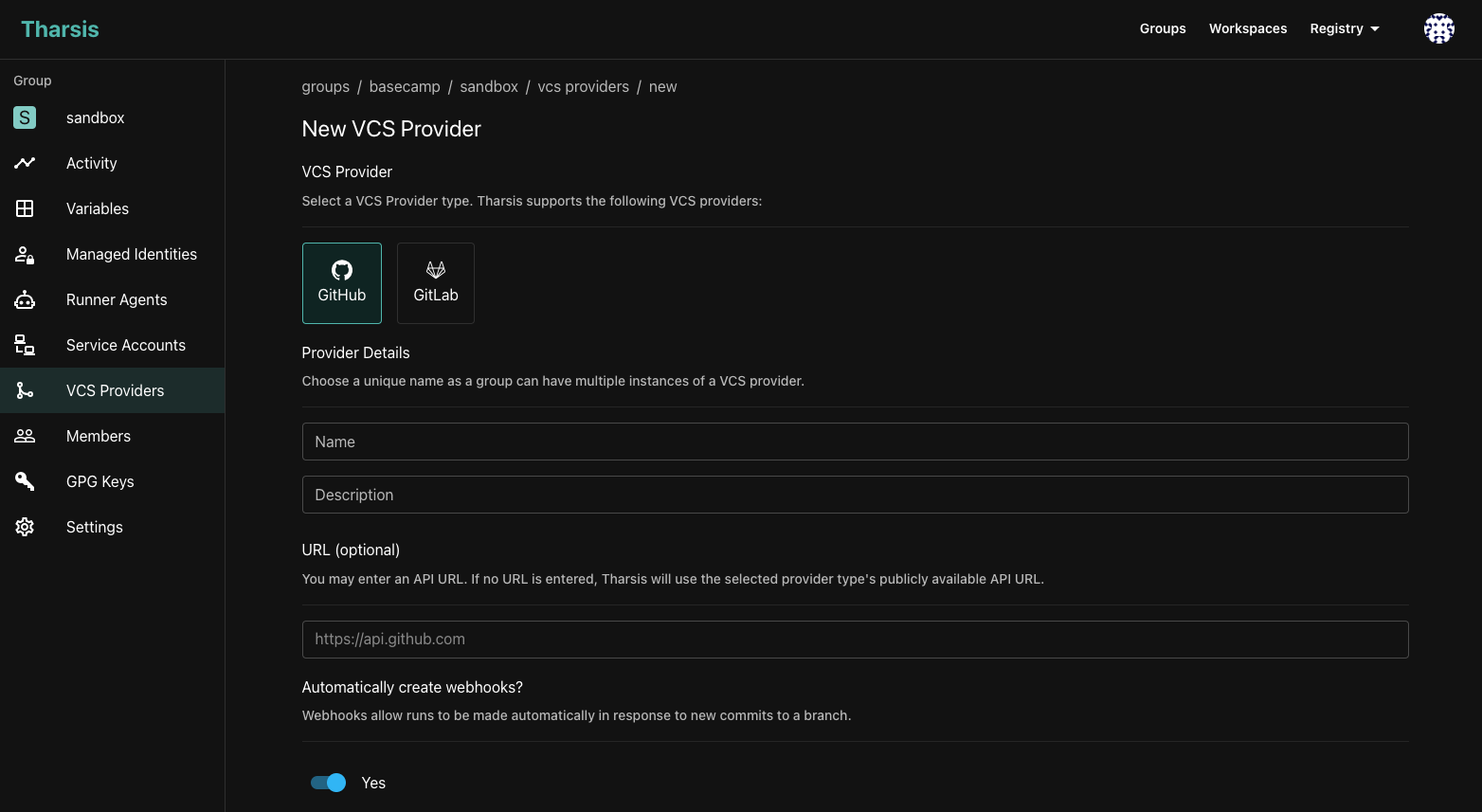
VCS Integration
Tharsis can integrate with your version control system (VCS) to automatically trigger Terraform deployments when changes are made to the code in your Git repository (both GitHub and GitLab VCS providers are currently supported). When a new commit is pushed to the repository, Tharsis will automatically create a new Terraform run for the workspace that is linked to the VCS provider. This allows you to automate your Terraform deployments and keep your infrastructure in sync with your codebase without having to manage CI/CD runners and pipelines.
Runner Agents
Runner agents are responsible for executing the jobs that will deploy your Terraform infrastructure. Runners use a pluggable job dispatcher to support various container runtimes such as Docker, Kubernetes, and AWS Fargate. The Tharsis API can be configured to use a shared runner agent that will pick up jobs from all groups and workspaces, or users can deploy a dedicated group runner agent that will only pick up jobs from the group that it's assigned to. This allows you to scale your runner agents horizontally by deploying multiple agents to handle the load of your deployments. It also allows runners to be deployed within a private network to access resources that are not publicly accessible.
Tharsis Terraform Provider
Tharsis includes a Terraform provider that allows you to interact with the Tharsis API from your Terraform code. This provider can be used to create and manage Tharsis resources via Terraform, and it includes a data source to consume outputs from other workspaces. The provider is available in the HashiCorp Terraform Registry.
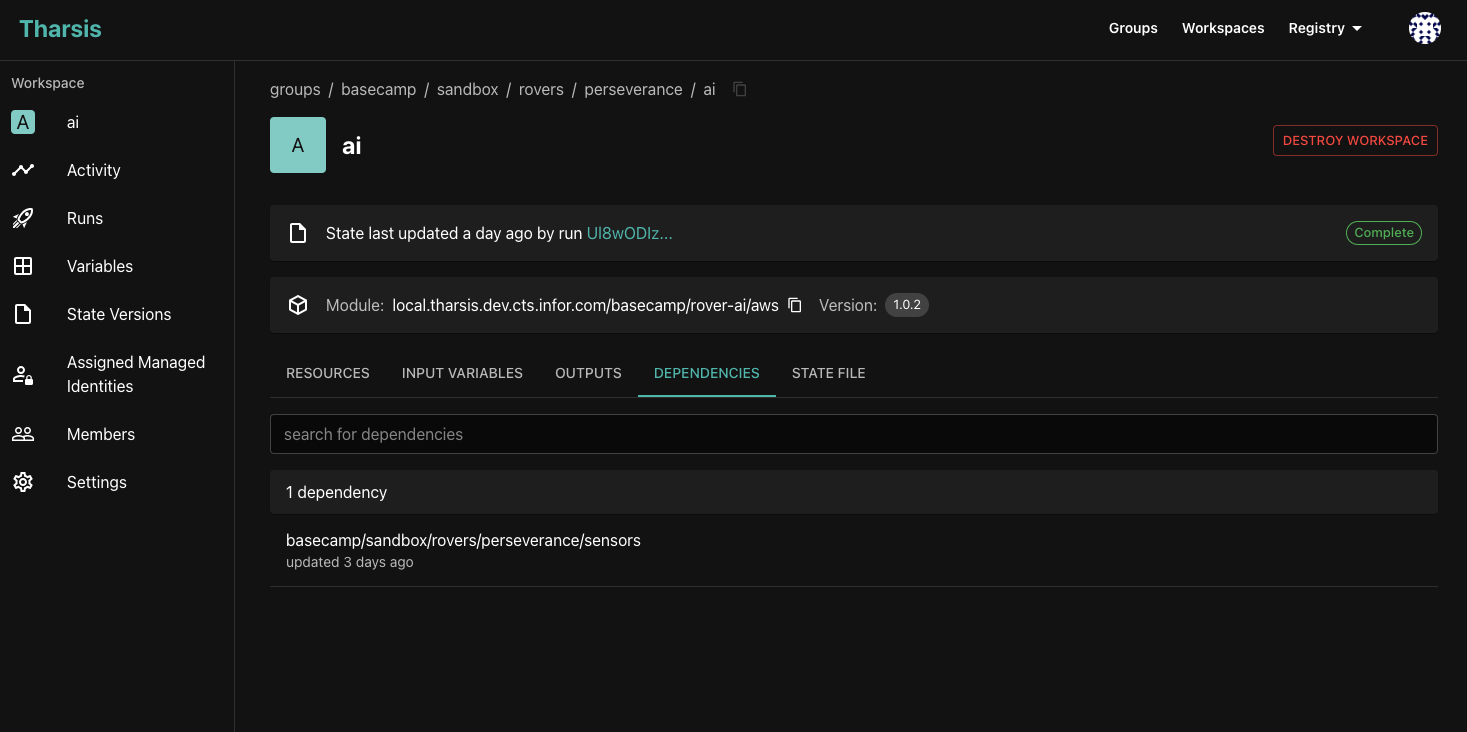
When using the Tharsis provider datasource to consume outputs from other workspaces, the UI will display any workspaces that the current workspace depends on. For example, in the screenshot below
the ai workspace depends on the sensors workspace because it's consuming an output from it.
Where do we go from here?
We are excited to share Tharsis with the community, and we are looking forward to your feedback. We have a lot of exciting features planned for the future, and we are looking forward to working with the community to make Tharsis the best open-source Terraform platform available.